MLT428
HISTOLOGICAL TECHNIQUES
SESSION 2021/2022
INTRODUCTION TO HISTOPATHOLOGY LABORATORY
PREPARED BY:
MUHAMMAD HAKIM BIN HASERI 2020480052
WAN AHMAD SYAHIR BIN HALIMI @ WAN HALIMI 2020620542
SITI NUR’AISYAH BINTI MUHAMAD HANAFEE 2020498568
NUR MAIZAN BINTI MOHD ZAINURI 2020621708
KU NORSAHIRA BINTI KU YAHYA 2020492762
PREPARED FOR:
MADAM HARTINI YUSOF & DR. NUR AYUNIE ZULKEPLI
INTRODUCTION
What is Histopathology?
Histopathology is the diagnosis and study of disease
of tissues which involving the examination of stained
tissue under microscope
Instruments in Histopathology Lab
Tissue transfer Setting panel Block holder Operating Setting panel Wax
basket (Inside)
Rotating Head & display handle & display reservoir Mold bin
Reagents Keypad controller
Blade cover Blade
{& wax Base(Body) holder
containers Stage
Cold plate Wax Forceps Tissue
dispenser warmer warmer
::
::
::
::
::
::
Tissue Processor ROTARY Microtome PARAFFIN WAX Tissue
embeddING CENTRE
BRAND: SHANDON CITADEL BRAND: SLEE MAINZ BRAND: SLEE MAINZ
MODEL: SHA 69800001
MODEL: CUT5062 MODEL: MPS/C / MPS/P / MPS/W
Tissue gROSSING
& fixation
Fresh Tissue specimen The specimen was grossed Tissue processing
and fixed with commercially
Tonsil/appendix/uterus/liver A process that give
specimens was obtained. prepared 10% formalin. rigidity to the tissue by
SLIDE mounting & using the tissue
labelling processor.
Mounting of the tissue slide with a Flowchart of Tissue embedding
coverslip and a mounting medium. General Procedure
Then the slides were labelled with Processed tissue is
surrounded in solidified
the required details. paraffin wax to make a tissue
block for tissue sectioning.
Tissue staining Tissue sectioning
A staining process of A process that give a
tissue section by using nice thin slice of tissue
H&E stain. section by using
microtome.
TISSUE GROSSING & FIXATION
Objective:
To gross the fixed tissue specimens into small blocks before it is processed using a tissue
processor.
Principle: Material:
Specimen is examined and dissected in correct Tonsil/appendix/uterus/liver specimens fixed with
size, thickness and orientation before being commercially prepared 10% formalin.
processed.
Equipment:
Ducted Fume Hood: Iryas
Apparatus: 5.Containers 9.Gloves
6.Rulers 10.Labcoat
1.Scalpel holders 7.Dissecting board 11.Mask
2.Scalpel blades 8.Medisheet 12.Goggle
3.Forcep
4.Tissue cassete
Procedure: Specimen grossing was performed
one at a time. The specimen was
Cassette was labelled according to sliced 2-3 mm thin with correct
the type of specimen with student orientation and was placed in the
name, student ID number and date
so that the specimen can be easily cassette.
identified.
The grossing workstation was prepared. The tissue cassette was
The fume hood lights and suction vent placed into 10% Neutral
Buffered Formalin to fix
switches were turned on and the
apparatus also were ensured to be ready. the specimen.
Result: Conclusion:
Tissue block After second cycle, nicely grossed
tissue block was obtained after
troubleshooting from the first cycle.
PrPoRObBlLeEMmSs SoSlOuLUtTioIOnNSs
Cassette cannot be closed - Slices the specimen thinner
tightly (2-3 mm)
- Do not overload the
cassette
TISSUE PROCESSING
OBJECTIVES
To provide sufficient rigidity to the tissue so that it can be cut into thin sections for microscopic
examination.
PRINCIPLES MATERIALS: Fixed tissue blocks
The water within the tissue is removed, and another (10% formalin)
medium (paraffin wax) is impregnated in the tissue
that provides the adequate support to the tissue. APPARATUS: Forceps, gl
oves, labcoat,
masks, goggles
1.Dehydration - remove water, aqueous fixative & REAGENTS:
lipids tissue fluids from tissues (alcohol)
2.Clearing - remove dehydrating agents & replace 10% Neutral Buffered Formalin,
with a fluid which is wax is soluble (xylene &
paraffin) Alcohol ( Absolute, 95%, 80%, 70%, 50%),
3.Impregnation - completely remove clearing Mixture of absolute alcohol & xylene,
agents & replace with wax that fully filled tissue
cavities (paraffin) Xylene, paraffin wax, distilled water
pROCEDURE 70% of alcohol 80% alcohol was 95% alcohol was
reagents was prepared prepared by adding prepared by adding
50% of alcohol 400ml distilled water 100ml distilled water
reagents was prepared by mixing 0.6L of to 1600ml absolute to 1900ml absolute
ditilled water to 1.4L
by mixing 1L of alcohol alcohol
absolute alcohol with absolute alcohol
All of the reagent is The mixture of xylene
1L distilled water prepared for 2L each mixture was prepared
& was placed in the by mixing 1L xylene to
Routine overnight processing
automated tissue 1L alcohol
No. Chemical/Reagent Time (hr) processor
1. Formalin 2:00
2. 50% alcohol 1:00
3. 70% alcohol 1:00 RESULT
4. 80% alcohol 1:00 Processed tissue block
5. 95% alcohol 1:00
6. Absolute alcohol 2:00
7. Absolute alcohol 2:00
8. Mixture of xylene & absolute alcohol 1:00
9. Xylene 2:00
10. Xylene 2:00
11. Paraffin wax 3:00
12. Paraffin wax 3:00
PROBLEMS SOLUTIONS CONCLUSION
Tissue block comes The lid of the casette did not After the first & second cycle of performing
out of the casette close tightly or the tissue is too tissue processing, the best quality of processed
while processing tissue blocks were produced by considering the
thick. Close the lid properly. time required of each process & making sure that
Tissue becomes too the reagents used for the processing are clean
soft after been Change the reagents and
processed. paraffin wax and usable.
TISSUE EMBEDDING
OBJECTIVE
To embed the tissue in a solid medium firm enough to support the
tissue and to prevent distortion of the tissue during cutting.
PRINCIPLE MATERIALS APPARATUS
Tissue is surrounded in a molten medium by using a Processed tissue blocks 1. Forceps
mould and let solidified to make a block for cutting 2. Scraper
thin section of tissue. The important functions of REAGENTS 3.Steel block mould
embedding medium are to give support of the tissue, 4. Gauze
to prevent distortion of the tissue during cutting and Paraffin wax 5.Tissue paper
to preserve the tissue for archival use. An ideal 6. Gloves
embedding medium should be molten between 30°C EQUIPMENT 7. Aprons
to 60°C, soluble in processing fluids, translucent or 8. Masks
transparent, suitable for sectioning and ribboning, Paraffin Wax Tissue
capable of flattening after ribboning, non-toxic, Embedding Centre: Slee
odorless, stable, easy to handle, homogenous and Mainz MPS/C / MPS/P /
inexpensive. MPS/W
The processed The Cryo PROCEDURE The best mould A small amount
tissue cassettes Console/Module was chosen of molten
was turned on A cassette was according to
were placed and the light taken and paraffin was
into the was turned on. opened to the size of the poured into the
view the tissue.
cassette bath. mould.
tissue sample.
The mould was transferred to a cold plate. The Processed tissue was transferred from the tissue
tissue flat was pressed firmly and gently with a cassette into the mould using warm forceps, with
pair of warm and clean forceps. Paraffin solidifies the cut surface facing downwards. The processed
in a thin layer that holds the tissue in position.
tissue was orientated accordingly.
The labelled The molten paraffin The mould was cooled slightly, and the labeled
cassette was was poured into the paper was placed on top of the cassette. The
placed on top of mould to fully cover the mould was cooled down immediately by placing
the mould. face of the cassette.
it on the cryo console.
The cryo console The excess wax was removed from paraffin The paraffin tissue block was
and light were tissue block cassettes and the used mould separated from its mould after
switched off.
was placed into a mould bath. the paraffin wax solidified.
PROBLEMS SOLUTIONS
RESULTS The surface of the block cracked Press the tissue on the wax
especially near the tissue. lightly and apply small pressure.
Paraffin block
Air bubbles are entrapped Slowly dispense the wax
around the tissue. during tissue embedding.
CONCLUSION
After several cycles of tissue embedding, the best tissue blocks are
obtained without crack and bubble around the tissue.
TISSUE SECTIONING
Objective: Principle:
To produce tissue sections with ideal thickness. Tissue is sliced into thin slices (3 microns thickness)
using the rotary microtome.
Material: Apparatus:
Paraffin block 1.Slide racks 7. Paper
8. Tissue paper
Equipment: 2.Clean frosted end 9. Pasteur pipettes
glass slide 10. Applicator sticks
1.Rotary microtome: Slee Mainz CUT5062 11. Pencils
2.Tissue floatation bath: XH-1001, Thermo Scientific 3.Microtome blades 12.Biohazards bag
4. Scraper
3120058 5.Clean brush
3. Freezer 6.Clean gauze
4. Oven
Procedure: The paraffin block The paraffin blocks was taken
was trimmed using off from the microtome and
The microtome was "Macro" setting (10
set up. been froze for 5 minutes
(Switch on, insert microns). using the freezer.
blade, adjust the
angle, set the mode) The tissue ribbon was laid on The paraffin blocks
the floatation bath which was was taken out and
The slide was labelled and set at 42-45°C and the fishing
allowed to dry on the slide technique was performed by sectioned with
rack at room temperature. microtome using
using glass slide. "Micro" setting (3
microns) until tissue
ribbon was obtained.
Result: Conclusion:
Tissue section on glass
slide. Thin and nicely cut tissue section which
attached perfectly on the glass slide will make
the staining process became so much easier.
PPRrOoBbLEleMmS s SSOoLlUuTtIOiNoSns
Tissue section wrinkled after Make sure the floatation bath
been laid on the floatation bath. temperature is 42-45°C.
Horizontal lines appeared Tighten the microtome
on the paraffin block. blade.
TISSUE STAINING
OBJECTIVE PRINCIPLE
To stain the tissue section using haematoxylin and The basic principle of H&E stain is the chemical
eosin (H&E) stain. attraction between tissue and dye. Hematoxylin, a
basic dye imparts blue-purple contrast on basophilic
MATERIALS APPARATUS structures, primarily those containing nucleic acid
components such as chromatin, ribosomes and
Unstained tissue slide Slide racks, forceps, cytoplasmic regions rich in RNA. The acidic eosin
filter papers, tissue counterstains the basic elements such as cytoplasm,
REAGENTS papers, funnel, muscle and collagen in varying intensities of pink,
Hematoxylin 3G (Sakura), measuring cylinder, orange and red.
eosin (Sakura), xylene, tripod stand.
alcohol (absolute, 95%),
distilled water, tap water.
EQUIPMENT
Oven: Memmert
Hotplate & Stirrer: Pro, HP-7 Lab Plus Series
Ductless Fume Hood: Esco
PROCEDURE
1. Dewaxing/ RESULT
Deparaffinization:
*Dip the slides at least 5 Tissue slide stained with H&E:
The unstained slides were times when transferring
removed from the oven from one reagent to another, A
(60°C for 30mins), or the to avoid shocking the tissue. A - Submucosa
hotplate (60°C for 3-
B B - Muscle fibres
5mins), then dipped into: C C - Collagen
Reagent: Time: 2. Hydration: D - Mucosa
xylene 3 mins
xylene 3 mins Reagent: Time: D E - Lymph nodules
xylene 3 mins 100% alcohol 1 mins
100% alcohol 1 mins E
95% alcohol 1 mins
Running tap 1 mins tonsil under 40x
water
3. Staining: Distilled water 1 mins CONCLUSION
Reagent: Staining of the transparent paraffin sections with
H&E stain provides colour contrast to allow the
Haematoxylin 3G Time: observation of the cell and tissue structure.
(Sakura) 5 mins 4. Dehydration:
Running tap Reagent: Time: PROBLEMS
water 5 mins 95% alcohol 10 secs 1.The tissue was stained too dark, hard to observe
under the microscope
Distilled water 30 secs 95% alcohol 10 secs
2.Tissue washed away from the slide, leaving a little
Eosin 2 mins 100% alcohol 1 mins or nothing on the slide.
Distilled water 10 secs 100% alcohol 1 mins SOLUTIONS
100% alcohol 1 mins 1.Make sure the time allocated for the slides in each
5. Clearing: staining reagent is correct, and not too long.
Reagent: Time: 2.Change the reagents- most manufacturers have
xylene 1 mins information as a guideline about the number of
xylene 2 mins slides that their reagents may tolerate before they
must be changed.
SLIDE MOUNTING & LABELLING
OBJECTIVE MATERIALS
To mount the tissue slide with a coverslip using a mounting H&E-stained tissue slides
medium.
To label the stained slide clearly with specimen and stain details. REAGENTS
PRINCIPLE Mounting medium
(CoverSeal-X), Xylene
The mounting medium isolates the sample from the outside and allows
better observation of the preparation under the microscope as it has APPARATUS
refractive properties similar to those of glass. Staining and mounting
reagents that are stable over extended periods of time, have strong Slide racks, coverslips, tissue
light-fastness, and are resistant to oxidative changes should be used. papers, Kimwipes, applicator
sticks, self-adhesive labels
sticker.
EQUIPMENT
Ductless Fume Hood: Esco
PROCEDURE louwTnheteirlecitdotgvoeeurncsthlliyepsawttah4se5° Swliditehstdwheeetarfeoilsllla:obweilnlegd aTnhde lsatbaeinlleedd
mounting medium. TSytpaienionfgsmpeecthimoedn osblidseerwveasd
wsaTishzeecohaofpsptheroenptaricisacstouerecdsoinevgcettrsioolitnph. e SSttuuddeenntt'nsaIDme muicnrdoesrctohpee.
nDuamteber
mAendaiudmeqwuaatsepmlaocuendtiongn Tthoeesnlsiduerewtahseerexaamreinneod
the slide, 1 or 2 drops. air bubbles trapped.
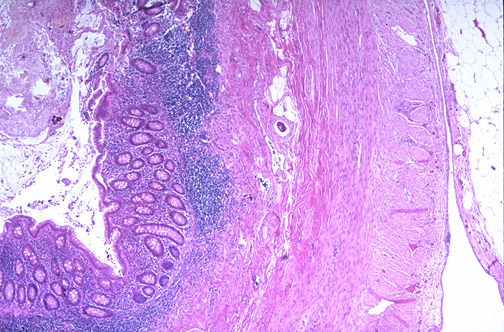
serosa
muscularis propria (externa)
collagen
submucosa
RESULTS crypts mucosa lymph
lumen appendix under 40x nodule
Mounted and labelled H&E-stained slide
CONCLUSION PROBLEMS SOLUTIONS
The mounting medium covers the Too many excesses of Try putting the medium on an
samples and fills the space mounting medium around unused coverslip to speculate the
between the slide and the the coverslip. adequate amount to be used.
coverslip, when the mounting Air bubbles are trapped Press the coverslip gently with an
medium hardens, it will provide under the coverslip. applicator stick to remove them.
rigidity and durability to the slide. Debris trapped under the Ensure the coverslip is clean before
coverslip. using, if not wipe it with Kimwipes.
FROZEN SECTION
OBJECTIVE glass slide display specimen EQUIPMENT material
door panel head
To learn and to practice the Cryostat: Slee Mainz Fresh tissue
frozen section method by MEV, Oven:
using the cryostat Memmert
control blade APPARATUS
panel holder
PRINCIPLE anti-roll hand wheel Brush, coplin jar, forcep,
plate coverslip, clean glass slides,
Water from the applicator stick, microtome
tissue will be converted freezing chamber
blade
into ice as the tissue goes CRYOSTAT REAGENTS
through the freezing process.
The ice will act as an embedding Tissue Freezing Medium / Frozen Section
media to allow the sectioning process. Compound, 10% Neutral Buffered Formalin,
Hematoxylin 3G (Sakura), Eosin (Sakura)
pp The cryostat was An hour before the The jar was removed The specimen was
rr set to -20°C. specimen arrived, a Coplin before sectioning grossed.
oo jar with 10% formalin was process.
cc
ee placed in the oven at
dd 60°C.
uu
rr The tissue was The tissue was trimmed The disc was placed in The tissue was
ee sectioned at 5µm at 10µm thick until the the orientable specimen embedded on a specimen
specimen was exposed. disc with Tissue Freezing
thick. head. Medium and was froze
in the cryostat.
The section was The slide then was Rapid H&E staining No. Chemical/Reagent Time
placed onto a labelled directly placed in the was performed.
slide. pre-heated 10% formalin 1. Absolute alcohol 10 dips
The slide was
for 1 minute. mounted. 2. Running tap Few dips
3. Haematoxylin 1 min
4. Running tap water Few dips
5. Distilled water 15 sec
6. Eosin 1 min
7. 95% Alcoh 10 dips
Adapted from Stephen, R. P. M. D. Microscopic examination 8. 95% Alcohol 10 dips
(2015) in Frozen Section Technique was performed.
9. Absolute alcohol 10 dips
10. Absolute alcohol 10 dips
11. Xylene 10 dips
result 12. Xylene 10 dips
13. Xylene 10 dips
conclusion Slide prepared
by
Frozen section is
performed when there is frozen section
a need for immediate Adapted from Stephen, R. P. (n.d.). in A Practical Guide to Frozen Section Technique.
diagnosis of lesions.
Using the cryostat, the problem solution
tissues will be frozen at
appropriate temperature Ice crystal artifacts can be observed on The cryostat must be set at an ideal
and sectioned for the
microscopic examination. the tissue temperature (-20°C)
The border of the tissue was seen to be After sectioning, the tissue must
indistinct during microscopic examination immediately be placed into 10% formalin
REFERENCES
Giri, D. (2018, November 6). Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Staining: Principle, Procedure and Interpretation.
LaboratoryTests.Org. http://laboratorytests.org/hematoxylin-and-eosin-staining/
Mayo Clinic. (n.d). Tissue Sectioning. Pathology Research Core. https://www.mayo.edu/research/core-
resources/pathology-research-core/services/tissue-sectioning
Mokobi, F. (2021, July 26). Hematoxylin and eosin stain (H and E stain or HE stain). Microbe Notes.
https://microbenotes.com/hematoxylin-and-eosin-stain/#principle
National University of Singapore. (n.d.). APPENDIX - NORMAL HISTOLOGY [Photograph]. APPENDIX - NORMAL
HISTOLOGY. https://medicine.nus.edu.sg/pathweb/normal-histology/appendix/
Rolls, G. B., & Sampias, C. C. J. D. (2019, August 14). H&E Staining Overview: A Guide to Best Practices.
Leica Biosystems. https://www.leicabiosystems.com/knowledge-pathway/he-staining-overview-a-guide-to-
best-practices/
Sampias, C. C. J. D. (2018, November 15). H&E Basics Part 4: Troubleshooting H&E. Leica Biosystems.
https://www.leicabiosystems.com/knowledge-pathway/he-basics-part-4-troubleshooting-he/
Stephen, P. (n.d.). The Art of Frozen Tissue Sectioning. Leica Biosystems.
https://www.leicabiosystems.com/knowledge-pathway/the-art-of-embedding-tissue-for-frozen-section/
Stephen, R. P. (n.d.). A Practical Guide to Frozen Section Technique. Springer.
https://www.garvan.org.au/research/capabilities/histopathology/files/a-practical-guide-to-frozen-section-
technique.pdf
Stephen, R. P. M. D. (2015). Frozen Section Technique. Pathology Innovations.
https://www.pathologyinnovations.com/frozen-section-technique
The Human Protein Atlas. (n.d.). Appendix [Photograph]. Appendix.
https://v15.proteinatlas.org/learn/dictionary/normal/appendix+1
Winsor L., Sluys R. (2018). Basic Histological Techniques for Planarians. In: Rink J. (eds) Planarian
Regeneration. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 1774. Humana Press, New York, NY.
https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-7802-1_9
The words you are searching are inside this book. To get more targeted content, please make full-text search by clicking here.
1.KU NORSAHIRA BINTI KU YAHYA (2020492762)
2.SITI NUR’AISYAH BINTI MUHAMAD HANAFEE (2020498568)
3.NUR MAIZAN BINTI MOHD ZAINURI (2020621708)
4.MUHAMMAD HAKIM BIN HASERI (2020480052)
5.WAN AHMAD SYAHIR BIN HALIMI @ WAN HALIMI (2020620542)
Discover the best professional documents and content resources in AnyFlip Document Base.
Search
HS2413B_HISTOLOGICAL LAB REPORT GROUP 4
- 1 - 11
Pages: